Copper price: After China ban, Australia had no problem finding new concentrate buyers
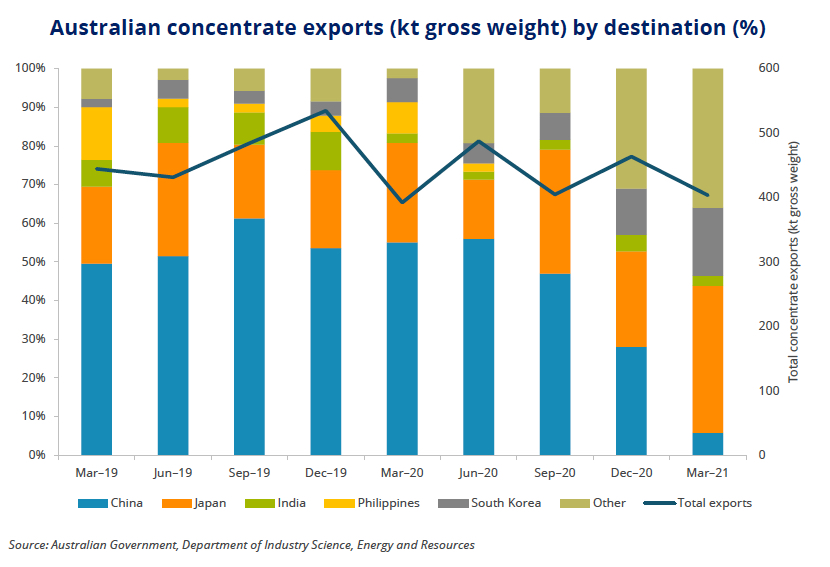
Unlike the iron ore market, where the countries’ steel mills and iron ore miners are joined at the hip, Australian concentrate only made up some 5% of Chinese imports. China was Australia’s no. 1 customer, however, and in the past sucked in more than half the country’s exports.
According to a new report by Roskill, a minerals and metals market research firm, total exports of Australian concentrates fell 8% in 2020 (in gross weight terms) as producers scrambled to find new customers in the final months of 2020.
It appears other Asian countries jumped at the chance to take up China’s slack. While Australia’s concentrate exports to China slumped 89% in the first quarter this year, Japanese and South Korean imports surged by 52% and 192% respectively.
Between them Japan and Korea purchased 56% of Australian exports of some 400,000 tonnes during Q1 2021, a 3% rise compared to the same quarter a year ago.
Refined exports jump
Treatment and refining charges (TC/RCs) paid by miners to smelters to process concentrate into refined metal rise when supply is ample and fall when smelters are forced to compete for scarce material.
TC/RCs have risen to more than $50 a tonne after falling to a historically low level of just over $20 a tonne in April in a sign that spot markets are loosening up. Today’s levies still compare to more than $70 a tonne in June last year and spikes as high as $130 in the previous decade.
Roskill says in addition to the change in countries buying Australian concentrates, production of primary refined copper in Q 1 2021 increased 20% and exports of refined copper (largely to China and Malaysia) increased 13%.
Copper prices turned higher again on Thursday, scaling $4.50 a pound or $9,920 a tonne in New York trading after falling back from a near two-month high on Monday. In Shanghai, copper was trading at a steep premium to Comex metal at CNY71,510 or around $11,050 a tonne.




