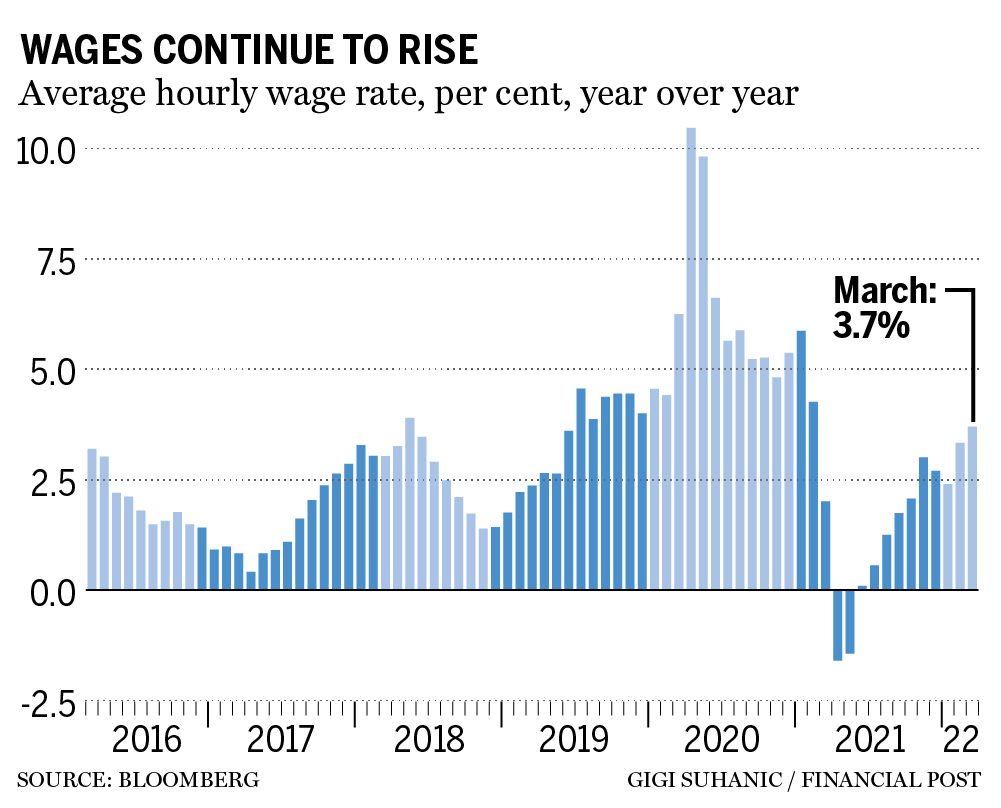Canada’s unemployment rate falls to record low of 5.3%

Kevin Carmichael: Latest numbers make it almost certain Bank of Canada will hike a half point next week

Article content
Before inflation surged last year, Bank of Canada governor Tiff Macklem was toying with the idea of testing the limits of full employment.
Advertisement 2
Story continues below
Article content
The jobless rate had spent much of 2019 around 5.5 per cent, and there had been no noticeable change in price dynamics, so maybe the limits could be probed by leaving interest rates low for longer. Macklem’s counterpart at the United States Federal Reserve, Jerome Powell, had been running a hot economy ahead of the COVID-19 crisis, and appeared to be successfully narrowing income gaps. It was reasonable to assume the strategy would work in Canada, too.
Macklem may yet get to perform a version of his experiment, although under much different conditions.
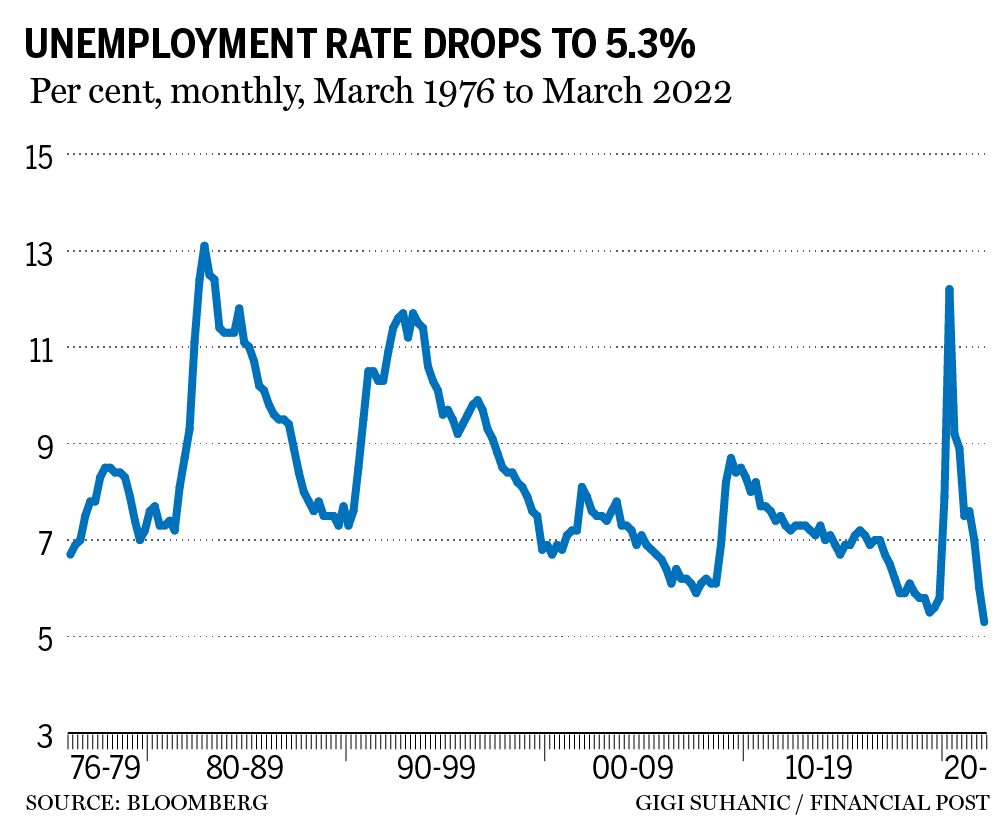
Canada’s jobless rate dropped to 5.3 per cent in March, a modern low, Statistics Canada reported on April 8.
But rather than marvelling at the power of monetary policy to reshape the labour market, Macklem and his deputies on Governing Council probably read the latest hiring numbers with a sense of apprehension. That’s because an inflationary episode that they initially diagnosed as an issue of supply is now equally a problem over over-stoked demand. The new data guarantee the Bank of Canada will accelerate its march to higher interest rates.
Advertisement 3
Story continues below
Article content
“With the unemployment rate so low, virtually all industries are bumping up against labour shortages, including those hospitality sectors that have yet to fully recover,” Nathan Janzen, assistant chief economist at Royal Bank of Canada, said in a note to clients. “With (extremely) tight labour markets and above-target inflation, there is no reason for the Bank of Canada to leave interest rates at emergency low levels.”
Employment rose by some 73,000 positions in March, Statistics Canada said. The unemployment rate fell from 5.5 per cent in February, which was more than enough to convince most economists that Canada had achieved “full employment,” a theoretical condition where everyone who wants a job can find one.
Advertisement 4
Story continues below
Article content
Few disagree with that assessment. Bank of Nova Scotia’s nowcast of real-time economic growth predicted a first-quarter increase of an annual rate of 5.1 per cent after it was updated with the new employment data, much faster than the Bank of Canada’s January outlook of about two per cent. Even Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland, who often holds up favourable hiring data as evidence of effective economic stewardship, now concedes that Canada’s economy is overstimulated.
“The time for extraordinary COVID support is over,” Freeland said in her budget speech on April 7.
The latest numbers show the labour market has rarely been tighter, which threatens to add to inflationary pressures by causing wages to spiral higher. Average hourly wages rose 3.4 per cent from March 2021, compared with a year-over-year increase of 3.1 per cent in February.
Advertisement 5
Story continues below
Article content
Statistics Canada reported that wages are increasing at a slower pace than the second half of 2019, when the jobless rate was hovering around 5.5 per cent and wages were increasing at an annual rate of around four per cent.
Nevertheless, policy-makers at the Bank of Canada, who are currently deliberating over their next policy update, will almost certainly decide to raise the benchmark rate by a half-point when they conclude their meetings on April 13. The consumer price index surged 5.7 per cent in February, the most in more than three decades and well outside the central bank’s comfort zone of one per cent to three per cent. The relatively muted wage increases could be sending a false signal, as pay raises are a lagging indicator.
Advertisement 6
Story continues below
Article content
-

Bank of Canada survey shows most businesses think it will take at least two years to get inflation under control
-

Economists predicting multiple half-point rate hikes by Bank of Canada
-

Why the Bank of Canada is now ‘talking tough’ on inflation
“The monetary policy implications are clear,” Karl Schamotta, chief market strategist at Cambridge Mercantile Corp., said in note to his clients. “With the economy now overshooting most measures of ‘full employment,’ wages accelerating, and prices continuing to rise, the Bank of Canada is widely expected to upgrade its inflation forecasts and hike rates by 50 basis points when it meets next week.”
• Email: kcarmichael@postmedia.com | Twitter: CarmichaelKevin
Advertisement
Story continues below