Bank of Canada holds interest rates at 0.25% but hints of hike to come

Kevin Carmichael: Bank declares end to economic emergency, promptly pivots to confront worst inflation scare in three decades

Article content
The Bank of Canada declared an end to the economic emergency caused by COVID-19, and promptly pivoted to confront the most serious inflation scare in more than three decades.
Advertisement
Story continues below
This advertisement has not loaded yet, but your article continues below.
Article content
Canada’s central bank concluded that the output gap, the difference between actual gross domestic product and the level of GDP that central bankers associate with the country’s non-inflationary speed limit, has closed ahead of schedule thanks to “robust” hiring, exports and investment.
For the Bank of Canada, that’s the equivalent of declaring, “mission accomplished.” Governor Tiff Macklem and his six deputies opted to end their commitment to keep the benchmark interest rate near zero until at least the spring, suggesting they will raise interest rates for the first time in more than two years when they next update interest-rate policy in early March.
“While COVID-19 continues to affect economic activity unevenly across sectors, the Governing Council judges that overall slack in the economy is absorbed, thus satisfying the condition outlined in the Bank’s forward guidance on its policy interest rate,” policy-makers said in a statement at the end of their latest round of deliberations on Jan. 26. “Looking ahead, the Governing Council expects interest rates will need to increase, with the timing and pace of those increases guided by the bank’s commitment to achieving the (two per cent) inflation target.”
Advertisement
Story continues below
This advertisement has not loaded yet, but your article continues below.
Article content
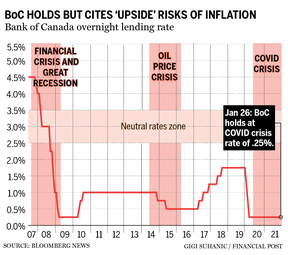
The central bank’s crisis-fighting efforts — backed by unprecedented fiscal stimulus on the part of the federal government — were remarkably successful in achieving their primary goal: crushing the deflationary forces that were triggered by the early stages of the pandemic, and avoiding a slow recovery like the one that followed the Great Recession. The Bank of Canada’s new quarterly economic outlook predicts gross domestic product (GDP) accelerated to an annual rate of 5.8 per cent in the fourth quarter, enough momentum to push through headwinds caused by the Omicron variant of COVID-19 and still produce growth of about two per cent in the current quarter.
Some economists think the Bank of Canada’s recession fight has been too successful. Ahead of the policy announcement, prices of financial assets linked to short-term interest rates implied that traders were betting on an immediate interest-rate increase, not a promise to do one within a couple of months.
Advertisement
Story continues below
This advertisement has not loaded yet, but your article continues below.
Article content
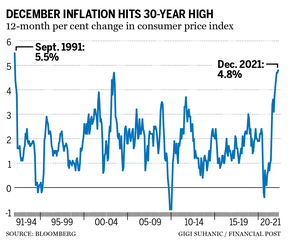
The consumer price index (CPI) surged 4.8 per cent in December from a year earlier, the biggest increase since 1991, which is when the Bank of Canada adopted a commitment to use the CPI to guide its interest-rate setting. The central bank’s target is two per cent, the midpoint of a comfort zone of one per cent to three per cent. Inflation has been outside the high end of that range since April, long enough for households and businesses to start thinking that high inflation will continue into the future.
Many traders and economists assumed the Bank of Canada would want to disrupt that psychology immediately with a sudden interest-rate increase. Macklem appears to have decided there was no need to panic. An interest-rate increase this week might have dented the central bank’s credibility, given it had been telling households and companies for the better part of two years that they could count on ultra-low borrowing costs until at least the middle of 2022.
Advertisement
Story continues below
This advertisement has not loaded yet, but your article continues below.
Article content
-

What you need to know about the Bank of Canada rate decision today
-

What a Bank of Canada rate hike could mean for mortgages and the housing market
-

Will rate hikes dampen Canada’s already lacklustre business investment?
-

Bank of Canada maintains interest rate: Read the official statement
Still, the central bank is hardly blasé about inflation. Its forecast has the CPI averaging year-over-year increases of 5.1 per cent in the first quarter before calming down over the second half as supply constraints ease. The central bank sees CPI inflation of 4.2 per cent in 2022 and 2.3 per cent in 2021.
“While the upside and downside risks to the bank’s inflation projection are viewed as roughly balanced, the upside risks are of greater concern,” the Bank of Canada said in its outlook. “Until inflation moves significantly lower, there is an elevated risk that Canadians will start to believe that inflation will stay high over the long term.”
Macklem balked at raising interest rates this week, but expect a steady march higher going forward. The next announcement is March 2.
• Email: [email protected] | Twitter: carmichaelkevin
Advertisement
Story continues below
This advertisement has not loaded yet, but your article continues below.









