Posthaste: Ever wonder why B.C. gas prices are so high? The answer might surprise you

New report highlights ‘worrying’ state of Canadian infrastructure

Article content

Ever pull into a gas station in British Columbia and wince at the posted price?
You’re not alone; since 2015, prices at the pumps in this western province have soared way above the national average. By 2023 you might have been paying 20 to 35 cents a litre more than you would in the rest of the country.
The good news is there is relief on the horizon; the bad news is how we got there in the first place.
Advertisement 2
Story continues below
Article content
The gas-price problem has been so bad that in 2019 the British Columbia Utilities Commission launched an investigation and concluded that price fixing was to blame.
But according to a report out this week from the C.D. Howe Institute, that probe was off the mark and the real culprit was an “invisible bottleneck” in the Trans Mountain pipeline.
“In diagnosing the issue of high gasoline prices, the B.C. government has mistakenly identified a case of insufficient pipeline infrastructure as an abuse of market power,” said G. Kent Fellows in his report.
Refined products like gasoline travel to British Columbia from Edmonton via the Trans Mountain pipeline, but since 2015 a “big squeeze” in this conduit has been responsible for B.C.’s pain at the pumps, he says.
As Fellows explains, a rule change that year by the National Energy Board, designed to stop producers from gaming the pipeline system, resulted in an increase in crude oil shipments and a reduction in refined product shipments.
A big reduction — the study says refined product shipments were basically cut in half, falling from 10,000 cubic metres a day to 5,000.
Article content
Advertisement 3
Story continues below
Article content
That meant gas wholesalers in British Columbia’s lower mainland had to find other ways to ship the gas they needed, and rail transport that is more expensive than pipeline was used to fill the gap.
The squeeze was costly. The report estimates that insufficient pipeline capacity has cost each British Columbian about $500 a year, or $1,200 a household — a “remarkable burden, particularly given the recent inflationary issues in Canada,” said Fellows.
Add it up and it cost B.C.’s economy $1.5 billion a year.
Fortunately, there is relief on the horizon. Since the opening of the Trans Mountain expansion in May that increased the pipeline’s capacity, “B.C. residents should see some gas-price relief,” said Fellows.
But the story of this “invisible” infrastructure squeeze is important because it is just the tip of the iceberg, he said.
“If we cannot even identify Trans Mountain’s Big Squeeze, we have no hope of identifying and mitigating the smaller ones,” he said. “There are other infrastructure bottlenecks across the Canadian economy.”
Michigan’s push to shut down Enbridge’s Line 5 pipeline is a problem that has not received enough attention, said Fellows. Closing that pipeline would create a shortage of 50 million litres of natural gas a day in Ontario and Quebec and a number of northern states.
Advertisement 4
Story continues below
Article content
The nation’s climate policy also relies heavily on electrification, but existing transmission and distribution networks will require a huge expansion to get there, he said.
Limitations on our existing road and rail system are already squeezing both domestic and international trade, yet Canada lacks a national transportation strategy, he said.
And then there is the high cost of building infrastructure in Canada.
The Trans Mountain expansion was estimated to cost just over $5 billion when it was first proposed, but the final bill was more than $30 billion.
“This is a problem,” said Fellows.
“As a country, Canada needs to do better.”
Sign up here to get Posthaste delivered straight to your inbox.
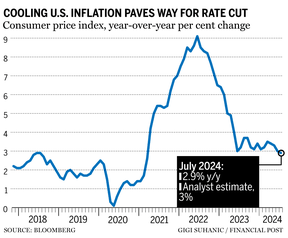
Inflation continued to cool in the United States, setting the Federal Reserve up for an interest rate cut next month.
“Overall the Fed will walk away from today’s release with more confidence that underlying inflation is headed in the right direction,” said Ali Jaffery, a senior economist at CIBC Capital Markets, in a note Wednesday.
After the data, markets were pricing in about 100 basis points of cuts this year, but bets on a bigger cut in September were easing.
Advertisement 5
Story continues below
Article content
“Markets are more focused on the risk of a recession and tomorrow’s retail sales report will have a greater influence on attitudes about the Fed than today’s inflation report,” said Jaffery.
CIBC expects three 25 basis-point cuts this year.
- Today’s Data: Canada existing home sales, United States retail sales, industrial production and NAHB housing market index
- Earnings: Walmart Inc., Deere & Co., Applied Materials Inc., Tapestry Inc.

Recommended from Editorial
In the artificial intelligence-fuelled era of the Magnificent Seven technology stocks, value investing has become wildly unpopular. Yet there are still good reasons to bother with value, writes Rob Arnott of the Financial Times. Here are four signs that value may well stage a stupendous comeback in the years ahead.
Advertisement 6
Story continues below
Article content
Are you worried about having enough for retirement? Do you need to adjust your portfolio? Are you wondering how to make ends meet? Drop us a line with your contact info and the gist of your problem and we’ll try to find some experts to help you out, while writing a Family Finance story about it (we’ll keep your name out of it, of course). If you have a simpler question, the crack team at FP Answers, led by Julie Cazzin, can give it a shot.
McLister on mortgages
Want to learn more about mortgages? Mortgage strategist Robert McLister’s Financial Post column can help navigate the complex sector, from the latest trends to financing opportunities you won’t want to miss. Plus check his mortgage rate page for Canada’s lowest national mortgage rates, updated daily.
Today’s Posthaste was written by Pamela Heaven, with additional reporting from Financial Post staff, The Canadian Press and Bloomberg.
Have a story idea, pitch, embargoed report, or a suggestion for this newsletter? Email us at [email protected].
Bookmark our website and support our journalism: Don’t miss the business news you need to know — add financialpost.com to your bookmarks and sign up for our newsletters here.
Article content












Comments